Design and Development of ECU using STM32F405
Design and Development of ECU using STM32F405
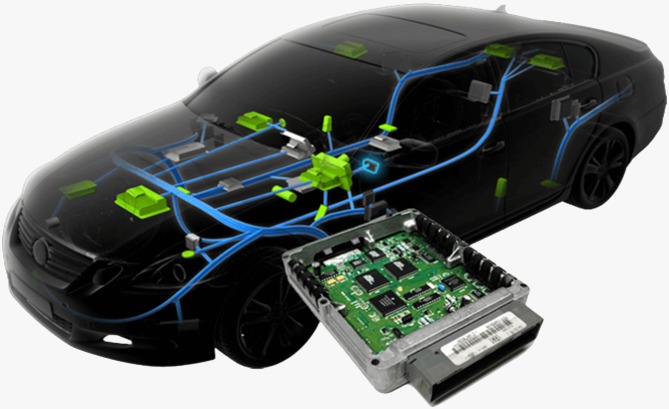
ECU’s are microcontrollers with I/O peripherals including sensors and actuators, that may accept input from the vehicle environment and carry out tasks in accordance with the functionality of the module that has been programmed by the OEM’s.
Automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) break down the entire vehicle operation into various modules for control. Every module has an Electronic control unit (ECU) that are used in vehicles to operate sophisticated control systems that improve the driving experience, safety & reliability.
ECU’s monitor various systems and provide warnings or take corrective action in case of any malfunction. ECUs have also made it possible for vehicles to be equipped with advanced features such as traction control, stability control, and anti-lock brakes.
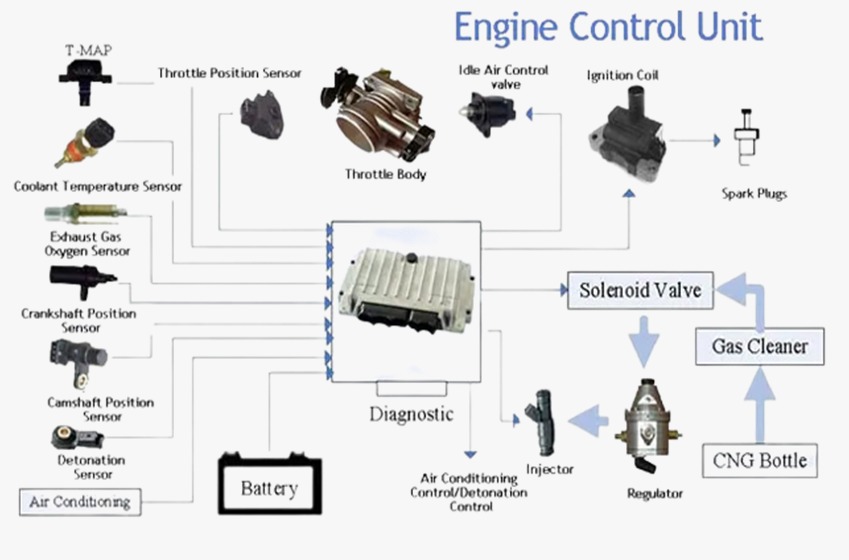

Different Types of ECU in Automotive Vehicles
Engine Control Unit (ECU) : The effectiveness and performance of the engine are managed by this ECU. It handles various engine operations including idle speed regulation and exhaust gas recirculation in addition to the air/fuel ratio and ignition timing.
Transmission Control Unit (TCU) : This ECU controls the transmission system in a vehicle, ensuring smooth gear shifts and optimal fuel efficiency. It also manages the clutch, torque converter, and other transmission components.
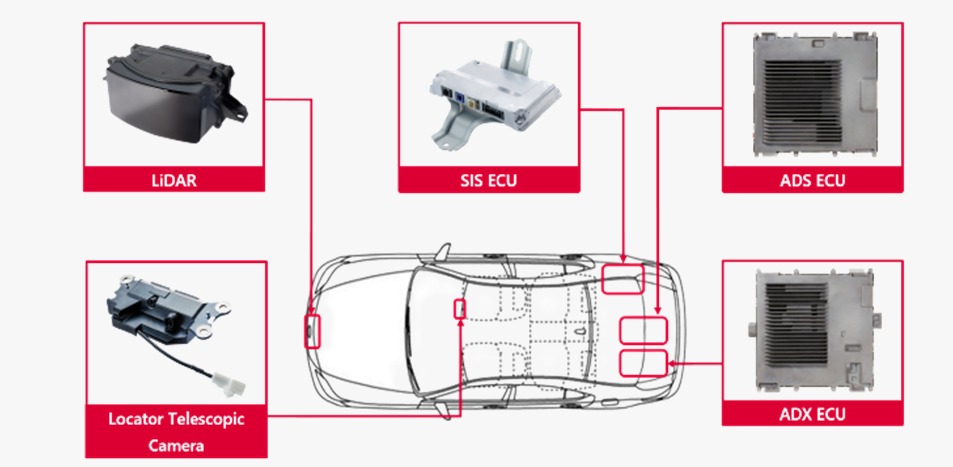
Brake Control Unit (BCU) : This ECU is responsible for controlling the braking system. It monitors the vehicle’s speed, brake pressure, and other data to ensure proper and safe braking performance.
Body Control Module (BCM) : Power windows, central locking, interior lighting and Infotainment are just a few of the comfort and convenience amenities that this ECU is in charge of managing in the car.
Suspension Control Unit (SCU) : The vehicle’s suspension system is managed by this ECU, which results in better handling and a more comfortable ride.
Climate Control Unit (CCU) : The climate control system of the car, including the air conditioning and heating, is managed by this ECU.
Navigation Control Unit (NCU) : This ECU is in charge of managing the navigation system in the car and giving the driver directions and other navigational data.
ADAS Control Unit (ADAS) : An ADAS ECU is a specific module that handles ADAS operations. Distributed ADAS ECUs are giving way to more centralized, integrated ADAS domain controllers. For vision and decision-making, the ADAS domain controller is the brain that integrates sensor input from cameras, lidar, radar, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and map data.
Telematics Control Unit (TCU) : This ECU is in charge of managing the telematics system in the car, which offers services like GPS tracking, remote diagnosis, and emergency assistance.
Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) : Direct TPMS alerts the driver of a vehicle when the air pressure in one or more tyres changes in a dangerous way. Each tyre is equipped with a pressure sensor transmitter that transmits readings to a central computer (ECU) for dashboard display.
Antilock Braking System (ABS) :A vehicle’s antilock braking system’s control module, or ABS, is a control unit that performs diagnostic tests and analyses data from wheel-speed sensors and the hydraulic braking system to decide when to release braking pressure at a wheel that is ready to lock up and begin sliding.In order to make sure the system works as it should, the ECU uses the processed data to generate electronic information.
Airbag Control Unit (ACU) :The airbag control unit analyses the data from the acceleration sensors to identify front, and rear-end collisions as well as the data from the pressure sensors to identify side collisions.
Hill Start Assist ECU : To prevent your car from rolling back unintentionally in a slope, the Hill Start Assist feature automatically maintains the pressure in the brake system for a brief period of time.
Electronic Stability Control ECU (ESP) :This ECU stabilizes your automobile when it starts to wander off your intended course, preventing loss of control in curves and emergency steering maneuvers. It automatically assists the driver in keeping the automobile under control during difficult steering maneuvers.
Seat Control and Comfort System ECU : This ECU integrates custom features like seat track adjustment, seat height and tilt adjustment and seat recliner adjustment. It also features seat position setting memory with recall algorithm, Seat ventilation and heating system
ECU Programming
ECU coding is the process of setting up particular options or settings in the ECU software. Options like the vehicle’s engine size, gearbox type, or reading particular parameters that the ECU has to handle like seat belt warning, engine idle etc., may fall under this category. We at VAct technologies have a customized embedded development board that can act as an ECU. The board comes with the following features:
- 2-Channel ECAN
- UART
- I2C
- SPI
Our customized development board based on STM32F405 has two onboard CAN interfaces making it possible to implement sending and receiving of CAN messages within the same board. Communication between two ECU’s with message filtering and prioritization is simulated in our training module. Our training module at VAct Technologies offers real-time exposure to simulate ECU functions like Electronic Stability Control, Blind Spot Detection, Digital Instrument Cluster, Collision Detection System and much more. Stay tuned for our next blog to know more about ECU development.
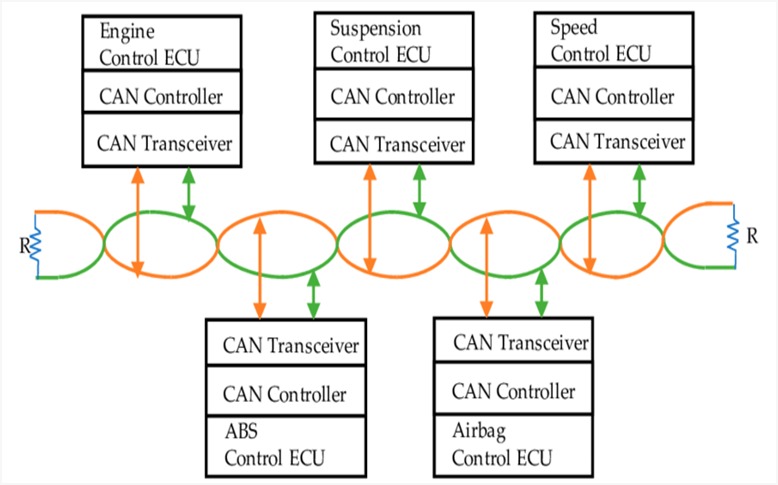
Final Thought
In conclusion, the Electronic Control Module, often known as the ECU, is crucial to the functionality and security of contemporary automobiles. Understanding how it works will help you appreciate the intricate planning that goes into each vehicle, ensuring that your trip is secure, efficient, and enjoyable.
