The Crucial Role of AI in Autonomous Vehicles
Introduction:
A revolution is taking place in the transportation industry, and artificial intelligence (AI) is at the forefront of it. Self-driving automobiles, also known as autonomous vehicles, have caught the attention of both tech enthusiasts and business professionals. These vehicles have the potential to revolutionize how we move, providing advantages in terms of convenience, efficiency, and safety. AI technology is at the center of this revolution and is essential to the development of autonomous vehicles.
How self-driving cars work:
AI powers the control systems in self-driving cars. Self-driving car developers integrate enormous amounts of data from image recognition systems with machine learning and neural networks to produce systems that can drive on their own.
The patterns that the neural networks identify in the data are then provided to the machine learning algorithms. One of the data sources the neural network uses to teach itself to recognize objects like traffic signals, trees, curbs, pedestrians, street signs, and other components of a given driving environment are images taken by self-driving car cameras.
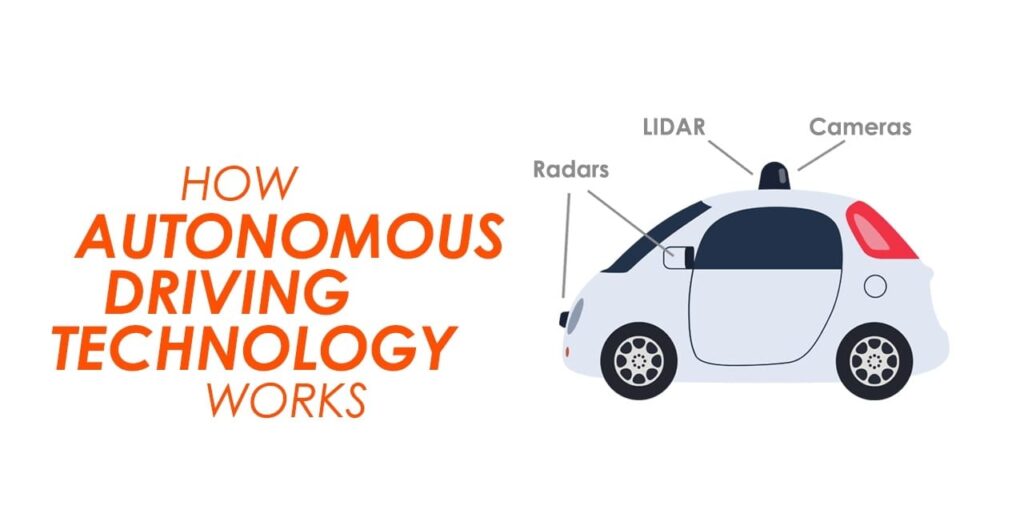
For instance, Google’s Waymo self-driving car project employs sensors, cameras, and lidar—a technology similar to RADAR—to recognize everything around the vehicle and predict what those items may do next. This happens in short bursts of time. The maturity of these systems is essential. As it gathers more driving data, the system can employ deeper learning algorithms to make more complex driving decisions.
The Foundation of Autonomous Vehicles: AI
1. Sensing the Environment
An autonomous vehicle’s capacity to observe and comprehend its surroundings is one of its most important capabilities. In this area, AI shines. AI algorithms use a variety of sensors, including lidar, radar, cameras, and ultrasonic detectors, to interpret enormous volumes of data in real time and produce a 360-degree image of the area around the car. These systems can distinguish objects, people, and other vehicles, and even forecast their future behavior thanks to machine learning techniques.
2. Decision-Making and Control
The car must decide how to navigate safely after gathering information about its surroundings. To choose the optimum course of action, such as accelerating, braking, or steering, AI systems examine the data. These choices are made using both machine learning models that have been trained on large datasets and predetermined rules. AI makes sure the car can adjust to shifting traffic circumstances and make quick decisions to prevent collisions.
3. Mapping and Localization
Accurate mapping and precise localization are essential for autonomous vehicles to navigate effectively. AI is employed to create detailed maps and to help the vehicle determine its exact position within those maps. Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) algorithms, often powered by AI, allow the vehicle to build and update maps in real-time as it moves through its environment, ensuring it always knows where it is.
4. Predictive Maintenance
AI isn’t limited to just driving capabilities. It also plays a significant role in the maintenance of autonomous vehicles. Sensors on the vehicle can monitor its mechanical components in real-time, and AI algorithms can analyze this data to predict when parts are likely to fail. This predictive maintenance not only improves safety but also reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
Levels of autonomy in self-driving cars:
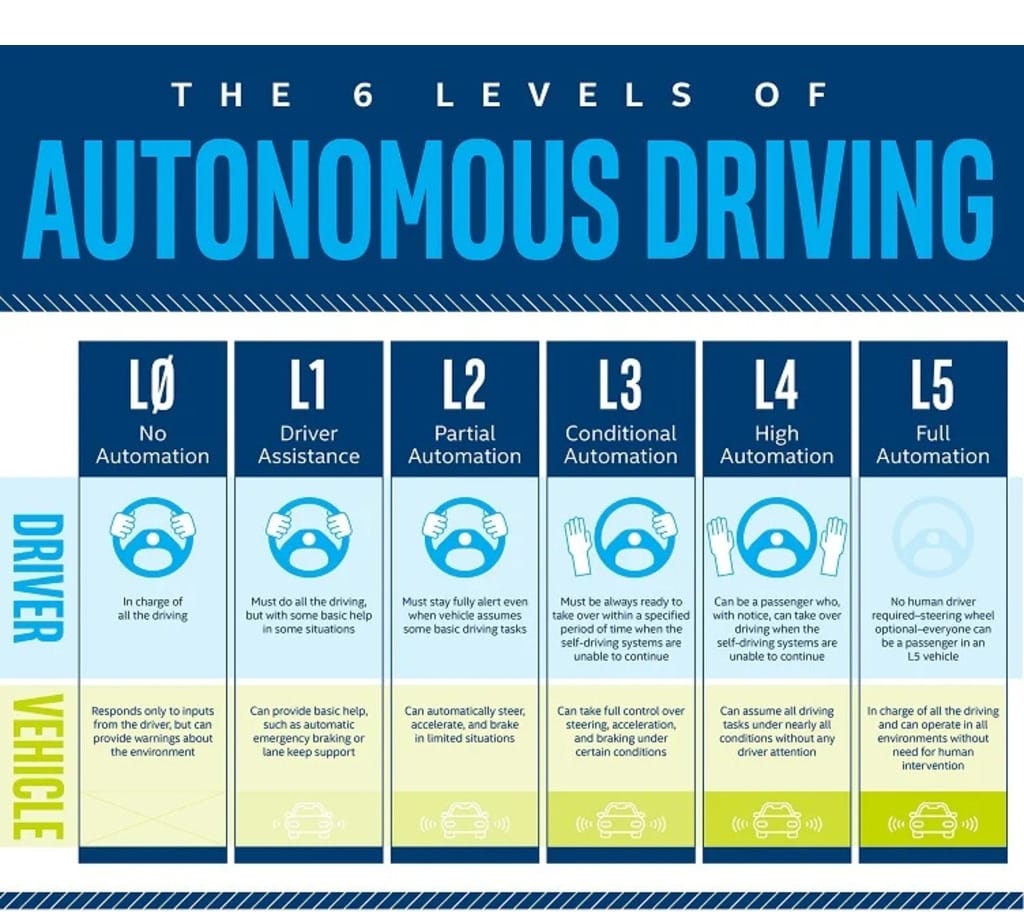
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) of the United States has defined six levels of automation, starting with Level 0—where humans still operate the vehicle—and progressing through driver assistance systems to completely autonomous vehicles. The following five stages of automation are as follows:
Level 1:
The human driver can receive assistance from an advanced driving assistance system (ADAS) with steering, braking, or acceleration, but not all at once. To warn drivers when they veer out of the travel lane, an ADAS combines rearview cameras and features like a vibrating seat warning.
Level 2:
An ADAS can steer and brake or accelerate at the same time while the driver is still fully conscious and operating the vehicle.
Level 3:
Under specific conditions, such as when parking the car, an automatic driving system (ADS) is capable of handling all driving duties. In these situations, the main driver of the car must still be a person who is prepared to regain control.
Level 4:
In some situations, an ADS is capable of handling all driving duties and keeping an eye on the roadside environment. The ADS is so trustworthy in those situations that the human driver is not required to pay attention.
Level 5:
In all situations, the vehicle’s ADS serves as a virtual chauffeur and handles all of the driving. The human occupants are only ever supposed to be passengers and never the driver.
Benefits of AI in Autonomous Vehicles:
1. Enhanced Safety: Autonomous vehicles, when equipped with AI, have the potential to significantly reduce accidents caused by human error, such as distracted or impaired driving.
2. Increased Efficiency: AI can optimize routes, reduce traffic congestion, and enhance fuel efficiency, ultimately saving time and resources.
3. Accessibility: Autonomous vehicles can provide mobility solutions for people with disabilities and the elderly, increasing accessibility for all.
4. Reduced Emissions: AI-driven autonomous vehicles can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by optimizing driving patterns and promoting electric or hybrid technologies.
Challenges and Future Directions
Although AI has a lot of potential for self-driving cars, there are still obstacles to be addressed. It is necessary to handle concerns like cybersecurity, moral conundrums (such as moral choices in emergencies), and regulatory frameworks.
AI skills are likely to continue to grow in the era of driverless vehicles. Expect improved user experiences, significantly safer and more effective self-driving cars, and a wider spectrum of uses outside personal transportation, such as autonomous delivery vehicles.
Conclusion
It is impossible to stress how important AI is to driverless vehicles. Self-driving cars are being developed as a result of AI technology, which gives them the ability to assess their surroundings, make judgments, maneuver precisely, and increase efficiency and safety. While there are still issues, the future of autonomous vehicles appears bright, and AI will continue to be a major influence on how we travel in the years to come.
